variable head permeability test derivation|falling head permeability test astm : Big box store In the laboratory we employ two methods. One is constant head permeability test. And another one is Falling head or variable head permeability test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed . A natureza não faz nada em vão. ️ me sigam @soyjujualves #brasil #memesbrasil #entretenimiento #usa #minasgerais
{plog:ftitle_list}
O Independiente Medellín jogará a próxima partida contra o .
In the laboratory we employ two methods. One is constant head permeability test. And another one is Falling head or variable head permeability test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed .
Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow .Constant head tests are most often carried out as inflow tests (where water is added to the borehole), but outflow tests (where water is pumped out of the borehole) can also be carried out. The equipment required is rather more . Chapter 48 - Falling head - Variable Head Permeability MethodThe property of the soil which permits the water or any liquid to flow through it through its vo.This test helps measure the permeability of soil, especially for less compacted types. The permeability impacts various aspects, such as settlement rates under loads, the design of .
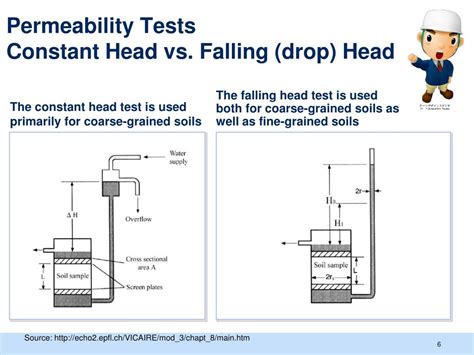
Discover the process of conducting a falling head permeability test for soil mechanics on YouTube.The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable .
falling head vs constant permeability
Abstract. When a monitoring well is tested for permeability, three methods, with three types of graphs, may be used to analyze the data of the water column Z (t) versus time t. .2.6 Permeability Tests 2.6.1 General - To determine the coefficient of permeability (or coefficient of hydraulic conductivity) k. - General method for determining k directly. 1) Constant-head .Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.2-2001; ASTM D5856) works the best.
Now a falling or constant head permeability test may be conducted, depending on the type of soil. The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for . Use of Pressure Derivative in Well Test Interpretation.” SPE Formation Evaluation . Variable Head Permeability Tests in Monitoring Wells: Comparing the Shape Factor Defined by Bouwer and Rice (1976) to the Shape Factor Given by Hvorslev (1951).” Geotechnical News .Determination of permeability in laboratory test is mostly used and significant impact to settlement of structure, control the earthen dams, maintain the well established , the routine laboratory test is used in current time which is consist the two types of test constant head permeability test and falling variable test.The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: 1.
The falling head permeability test, also called the variable head test, is a common way to test the permeability of relatively fine soil in a laboratory. In .
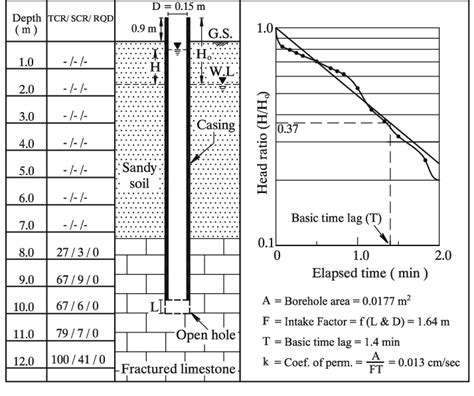
This video shows how to perform a falling head permeability test for fine-grained soil. This test is typically performed on fine-grained soil with low permea.It is a valid test for soils with a high rate of flow like sands and gravels, but also some clay soils. Falling Head Test allows the head to decrease as water infiltrates the sample, diminishing the pressure over the course of the test. Falling head methods are generally limited to fine-grained soils. Soil Permeability Testing Equipment In addition, one book presents a test in an aquitard as an example of test in an aquifer. The H 0 value was easily found by the optimization method for all tests, and the derivative graph for 19 of the 21 tests, two data sets being too inaccurate to yield a good derivative graph.Figure 12.9 Analysis of variable head tests. For the generic case of a cylindrical test zone of length L and diameter D (Figure 12.11), where LID > 10 (as stated in BS EN ISO 22282-2:2012), permeability from variable head tests can be calculated as. where d is the diameter of the section of tubing within which the water level rises and falls.
Non-steady flow in the variable-head permeability test Open PDF. Géotechnique. ISSN 0016-8505 | E-ISSN 1751-7656. Volume 55 Issue 9, November 2005, pp. 703-703. Prev Next > Non-steady flow in the variable-head permeability test . This method, also called the Variable Head Permeability test, is suitable for fine grain soils with intermediate-low permeability such as clays and silts. . This test refers to the Constant head permeability method. At the time of writing, VJ Tech complies to BS1377-6:1990, EN ISO 17892-11 and D5484-16 (Method A). a. Sample Preparation.
This definition explains the meaning of Falling Head Test and why it matters. #.. Table of Contents . A falling head test is one of the variable head test procedures that is undertaken in-situ in a borehole to determine the permeability of the soil. The falling head test is carried out for permeable soils and requires knowledge of the .There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: (1) the constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s). GATE ACADEMY Global is an initiative by us to provide a separate channel for all our technical content using "ENGLISH" as a primary language of communication.6.4 Presentation of Results : The permeability values are reported at T0C and 270C. The state of sample is also reported in terms of water content, void ration and degree of saturation. 7. Video Constant Head Permeability Test Falling Head Permeability Test 8. Download Download PDF
А2.4 VARIABLE HEAD (FALLING AND RISING HEAD) TESTS - CALCULATION OF PERMEABILITY VALUES. The permeability k may be determined for a variable head test using the following formula: where. A is the cross-sectional .
Falling Head Permeability Test. This is also known as the Variable head permeability test. The head-causing flow in this method is not as constant as in the previous method. The falling head permeability test is employed for the permeability of soil like fine-grained soil, and clay. Fig.2. Falling Head PermeameterDarcy’s Law describes how head, hydraulic gradients and hydraulic conductivity are linked to quantify and describe groundwater flow. For example, to compute the discharge of groundwater (Q) through a cross-sectional area of sand below the water table that is 100 m by 30 m (A) with a hydraulic conductivity of 15 m/d (K), and with a head change (Δh) of -2 m over a flow path .
IIT Gandhinagar, Soil Mechanics Lab Page 1 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY GANDHINAGAR Department of Civil Engineering Soil Mechanics LaboratorySituation 1 For a variable head permeability test, the following data were given: Length of specimen= 37.5 cm; Area of specimen= 19.4 sq.cm; Coefficient of permeability= 0.002912 cm/sec. 2 points What should be the area of the standpipe for the head to drop from 63.5 cm to 30.5 cm in 8 minutes?
In the falling head permeability test, in the duration of 3 hours the initial head of 1000 mm is dropped to 350 mm. The diameter of the stand pipe is 0.5 cm.
PART I. CONSTANT-HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used primarily to. determine the suitability of sands .
2.6.3 Falling Head Permeability Test Figure 12-2 - For cohesive soils with low permeability, flow quantity is very small. Ex) For soils with k = 1×10-6 cm/min ⇒ Flow quantity = .0972 cc/hr for i=20 and A = 81 cm2 (small amount of flow quantity and longer duration time) Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to interpret such tests. Abstract. Field permeability tests gave the local hydraulic conductivities (K) at three different sites. Constant head (CH) and variable head (VH) tests were performed using 33 monitoring wells (MWs) installed in confined aquifers. Each test method was conducted with either an inward flow from aquifer to pipe or outward flow from pipe to aquifer, which makes a .PERMEABILITY TEST A. CONSTANT HEAD OBJECTIVE. To determine the coefficient of permeability of a soil using constant head method. need and Scope The knowledge of this property is much useful in solving problems involving yield of water bearing strata, seepage through earthen dams, stability of earthen dams, and embankments of canal bank affected by .
falling head tests in borehole
WEBto watch in your location. Customers also watched. Subscribe. Este mocumentário acompanha os vampiros Viago, Deacon, Peter e Vladislav, que dividem um apartamento em Wellington e tentam se manter .
variable head permeability test derivation|falling head permeability test astm